KJC Medicinal Garden
Nocchi
Vitex negundo
Order: Lamiales
Family: Lamiaceae
Genus: Vitex
Species: V. negundo
Common Names: Chinese Chaste Tree
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
i. Vitex Trifolia
ii. Vitex Rotundifolia
- Vitex negundo is an erect shrub or small tree growing from 2 to 8 m (6.6 to 26.2 ft) in height.
- The bark is reddish brown. Its leaves are digitate, with five lanceolate leaflets, sometimes three.
- Each leaflet is around 4 to 10 cm (1.6 to 3.9 in) in length, with the central leaflet being the largest and possessing a stalk.
- The fruit is a succulent drupe, 4 mm (0.16 in) in diameter, rounded to egg-shaped. It is black or purple when ripe.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- Vitex negundo is used for treating stored garlic against pests and as a cough remedy.
- It is used in traditional herbal medicine for women's health, including treatments for regulating the menstrual cycle, fibrocystic breast disease and post-partum remedies.
- The leaves of Vitex negundo L. are known to possess various antioxidant chemical constituents like flavonoids, vitamin C and carotene, which might possibly be responsible for the reduction of lipid peroxidation production.
- Vitex negundo is typically known for its role in the modulation of cellular events like apoptosis, cell cycle, motility of sperms, polycystic ovary disease, and menstrual cycle. VN, reportedly, perturbs many cancer-signaling pathways.
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Leaves: The leaves Vitex negundo L are Antibacterial; Antitumor, Astringent, Febrifuge, Sedative.
- Stem: A decoction of the stems of Vitex negundo L is used in the treatment of burns and scalds.
- Fruit: The fruit is also used in the treatment of angina, cold, cough, rheumatic difficulties.
- Root: It is used in the treatment of cold and rheumatic ailments.
Active Phytochemicals
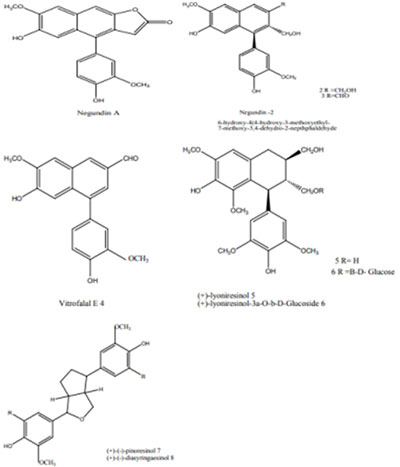
Phytochemical investigation of this plant indicated the presence of monoterpenes agnuside, flavonoids- casticin, chryso-splenol and vitexin, flavonoids (vitexicarpin) also, 5,3’-dihydroxy-3,6,7,4’-tetramethoxyllavone and hydroxy-3,6,7,3’,4’-penta methoxy flavone from the leaves (13). Seeds of Vitex negundo L agorded a new lignan characterized as 6-hydroxy-4-4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl), 3-hydroxymethyl-7- methoxy-3,4-dihydro-2-naphthaldehyde by spectroscopic methods and triterpenoids (betulinic acid and ursolic acid), lignans (negundins, vitedonin), alkaloid (vitrafalal) and diterpene (vitedoin) investigated.
References
[1] Gill BS, Mehra R, Navgeet, Kumar S. Vitex negundo and its medicinal value. Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):2925-2934. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4421-3. Epub 2018 Oct 11. PMID: 30311123.
[2] Dharmasiri MG, Jayakody JR, Galhena G, Liyanage SS, Ratnasooriya WD. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of mature fresh leaves of Vitex negundo. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003 Aug;87(2-3):199-206. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(03)00159-4. PMID: 12860308.


