KJC Medicinal Garden
Nirulakki
Vitex trifolia
Order: Lamiales
Family:Lamiaceae
Genus: Vitex
Species: V. trifolia
Common Names: Jalanirgundi, Sindhuka, Surasa, Vrikshaha, Nichinda, Niruvavili
Native to: Naturally found along coastlines from tropical East Africa as far east as French Polynesia
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
V. agnus-castus
V.negundo
V.doniana
V. peduncularis
V. quinata
V. payos
- Shrub or small tree; young branches densely pubescent with greyish hairs
- Leaves 1–5-foliolate; leaflets oblong-elliptic to oblanceolate or obovate or almost round, 1.5–7 x 0.8–4 cm, emarginate or rounded to acute or acuminate at the apex, cuneate to attenuate at the base, puberulous to glabrescent and ± glandular above, tomentose beneath; petiole 0.6–3.3 cm long; petiolules 1–20 mm long.
- Inflorescences terminal, usually together with axillary ones from the upper axils, much-branched, paniculate.
- Calyx 4–5 mm long, white tomentose outside
- Corolla blue to purple, puberulous outside; tube 10–13 mm long; lower lip up to 6 mm long.
- Fruit globose or ovoid, c. 5 mm in diam.; fruiting calyx cup-shaped, c. 5 mm wide.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- The leaves are used to treat female ailments in the Cook Islands, and used to relieve fever in Samoa.[citation needed] Additionally in Samoa, the dried leaves are burned to deter mosquitos
- It is used for curing ailments like fever, stomach related issues, rheumatic pain and problems caused due to inflammation.
- The leaves contain 0.11 - 0.28% of an essential oil and a resin. The chief constituents of the oil are l-d pinene and camphene, which between them constitute 55% of the oil, there is also 10% terpinyl acetate and 20% of a diterpene alcohol.
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Anti-bacterial
- Anti-fungal
- Anti-microbial
- Anti-tubercular
Active Phytochemicals
Diterpenoids
A new halimane diterpenoid, 13-hydroxy-5(10),14-halimadien-6-one (1) and two new labdane diterpenoids, 6α,7α-diacetoxy-13-hydroxy-8(9),14-labdadien (2) and 9-hydroxy-13(14)-labden-15,16-olide (3), were isolated for the first time, along with fifteen known compounds, from the hexane soluble fraction of methanolic extract of Vitex trifolia leaves. The structures of these new diterpenoids were elucidated by spectral analysis. Their relative configurations were established using analysis of NOESY correlations and coupling constants observed in (1)H NMR. Compounds 2, 3 and another known diterpenoid, isoambreinolide (4) were evaluated for antitubercular activity. 3 and 4 exhibited antitubercular activity (MIC=100 and 25 μg/ml) against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv in BACTEC-460 assay.
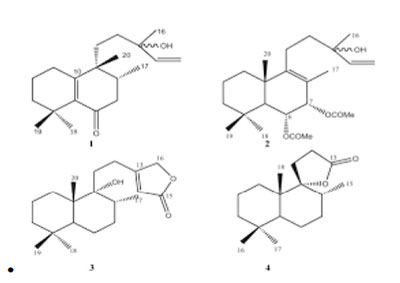
Triterpenoids
Five triterpenoids were obtained and identified as ursolic acid (I),2alpha,3alpha-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid (II), betulinic acid (11), taraxerol (IV), 2alpha,3beta, 19-trihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid (V).
Flavonoids
Six flavonoids, persicogenin (1), artemetin (2), luteolin (3), penduletin (4), vitexicarpin (5) and chrysosplenol-D (6), have been isolated for the first time as new cell cycle inhibitors from Vitex trifolia L
References
https://medcraveonline.com/MOJBOC/an-overview-study-on-chemical-constituents-and-biological-activities-of-vitex-peduncularis-wall.html
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21049612
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16087636/#:~:text=Six%20flavonoids%2C%20persicogenin%20(1),a%20bioassay%2Dguided%20separation%20procedure.
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Vitex+doniana


