KJC Medicinal Garden
Hebbevu
Swietenia macrophylla
Order: Sapindales
Family: Meliaceae
Genus: Swietenia
Species: S.macrophylla
Common Names: Mahogany, Honduran mahogany
Native to South America,Mexico and Central America
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
S.humilis
S.mahagoni
- Tree with tall straight (50-60 cm tall), cylindrical bole clear of branches for 12-18m
- Leaves: Simple, dark green or yellowish green, asymmetrically lanceolate, apex shortly acuminate,tapered leaf tip, pinnate venation
- Seeds are chestnut colored and 7.5-12cm in length
- Flowers: Green yellowish, corolla with 5petals, monoecio
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- Used for detoxification and immune function of the body
- Leaves, seeds, bark extract are used for the treatment of hypertension,diabetes, relieve pain, malaria and various skin condition
- In Bolivian Amazonian the seeds are used for leishmaniasis and as an abortion medicine
- The fruit, commonly called as Sky fruit which has been used commercially in healthcare products to improve blood circulatio
- Minerals- Nitrogen & Phosphorus
- Calcium: 10 mg; Phosphorus:19.5 mg; Iron:0.25 mg
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Anti-fungal activity
- Anti-diarrhoeal activity
- Hypoglycaemic activity
- Anti-bacterial activity
- Cytotoxic activity
- Anti-inflammatory activity
- Anti-hepatitis C activity
- Anti-malaria and Anti-babesia activity
- Anti-tumor and Anti-mutagenecity activity
- Anti-feedent activity
- Anti-noiceptive activity
Active Phytochemicals
1. Limonoid
Limonoid are phytochemicals of the triterpenoid class which are abundant in sweet or sour-scented citrus fruit and other plants of the family of Meliaceae. A wide range of biological activities for these compounds, including insect anti-feedant and growth regulating properties, a variety of medicinal effects in animals and humans, and anti-fungal, anti-bactericidal, and antiviral activity.
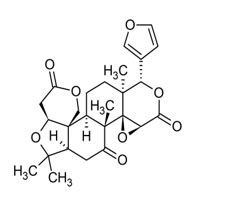
2. Tetranortritrepanoids (4,4,8-trimethyl-17-furanyl)
Neem, Azadirachta indica A. Juss (Meliaceae) seeds contain a number of complex triterpenoids which are of great interest as they exhibit a variety of biological properties. Several of these contain UV chromophores such as α,β - unsaturated ketone, furan, α,β -unsaturated ester and tigloyl groups. The bio-efficacy of neem formulations is altered due to degradation of the triterpenoids under light exposure. Hence, it is relevant to study the formation, isolation and bio-activity of the products formed when pure samples of these limonoids are exposed to sunlight. Herein the photolysis of salannin, one of the major triterpenoids present in the neem seed.
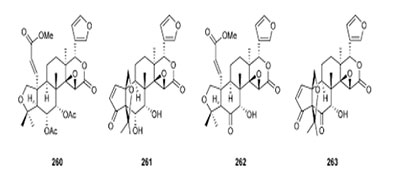
3. Poly-phenol
4. Swietenoloide (3,6-O,O-diacetylswietenolide)
5. hexadecanoate
6. Cadina-1,4-diene
7. Methyl-6-β-hydroxyangololensate
8. 6-O-acetylswietephragmin E
9. 2,11-diacetoxyswetenialide D
10. Liganin (3-hydroxycaruilignam)
11. β-sitosterol
12. Phragmalin8,9,14-orthoacetate
References
Moghadamtousi, Soheil Zorofchian, Bey Hing Goh, Chim Kei Chan, Tara Shabab, and Habsah Abdul Kadir. "Biological activities and phytochemicals of Swietenia macrophylla King." Molecules 18, no. 9 (2013): 10465-10483
Gullison, R. E., S. N. Panfil, J. J. Strouse, and S. P. Hubbell. "Ecology and management of mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King) in the Chimanes Forest, Beni, Bolivia." Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 122, no. 1 (1996): 9-34
Eid, Ahmad Mustafa Masoud, Nagib Ali Elmarzugi, and Hesham Ali El-enshasy. "A review on the phytopharmacological effect of Swietenia macrophylla." seeds 3 (2013): 5