KJC Medicinal Garden
Hippali
Piper longum
Order: Piperales
Family: Piperaceae
Genus: Piper
Species: P. longum
Common Names: Long pepper, Indian long pepper ,pipli
Native to
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
P. auritum (Sacred Pepper)
P. aduncum (Spiked Pepper)
P. betlle (Betel Pepper)
P. sarmentosum (Wild Pepper)
P. guineense (Ashanti Pepper)
P. nigrum (Black Pepper)
P. cubeba (Java Pepper)
- Climber: Scandent or straggling shrubs, sometimes ascending and climbing
- Leaves: The leaves are 5-9 cm long and 5 cm wide, lower leaves are broadly ovate, upper leaves are dark green and cordate with short petiole.
- Flowers: Flowers are unisexual arranged in erect spikes. Female spikes are 1.25-2.00 cm long and male spikes are longer, slender and are 2.5-7.5 cm long.
- The young shoots are drooping type.
- It gives rise to multiple fruit, which is shining dark green when immature and blackish-green when fully mature.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- Plant root is used in Ayurveda as a carminative, tonic to the liver, stomachic, emmenagogue, abortifacient and aphrodisiac.
- Fruits contain haematinic, diuretic, digestive and general tonic properties, besides being useful in inflammation of the lever, pains in the joints, snakebite, scorpion sting and night blindness.
- The plant is also used in dyspepsia, abdominal pain, anorexia, asthma, fever and act as anti-haemorrhoidal and appetiser.
- Immunomodulatory activity
- Gastroprotective activity
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Anticancer
- Antimicrobial
- Analgesic
- Antifungal
- Antimicrobial
- Antiviral
Active Phytochemicals
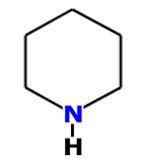
1. Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic molecule, heterocyclic amine that consists of five methylene bridges and one amine bridge. The name comes from the genus name Piper, which is the Latin word for pepper. The piperidine structural motif is present in numerous natural alkaloids such as natural occurring solenopsins. These include piperine which gives black pepper its spicy taste. Other examples include fire ant toxin solenopsin, the nicotine analog anabases of tree tobacco and the toxic alkaloid coniine from poison hemlock which was used to put Socrates to death. Its derivatives are ubiquitous building blocks in pharmaceuticals, like Icaridin (Insect repellent), SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), SERM (selective estrogen receptor modulators)
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
Flavenoids are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
References
Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity of Pepper (Piper nigrum L.) against some human pathogens P. Ganesh, R. Suresh Kumar and P. Saranraj
Fungicidal activity of pipernonaline, a piperidine alkaloid derived from long pepper, Plongum L., against phytopathogenic fungi Sung-EunLeeaByeoung-SooParkaMoo-KeyKimaWon-SikChoibHeung-TaeKimcKwang-YunChocSang-GueiLeedHoi-SeonLeea

