KJC Medicinal Garden
Kodasige
Holarrhena pubescens
Order: Gentianales
Family: Apocynaceae
Genus: Holarrhena
Species: H. pubescens
Common Names: Indrajao, Indra’s seed
Native to Central and southern Africa, the Indian Subcontinent, Indochina, and parts of China.
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
H. congolensis
H. curtisii
H. floribunda
H. mitis
H. pubescens
- Shrub (9–18) m tall, with abundant white latex in all parts, bark in young trees nearly smooth, later corky, longitudinally fissured.
- Leaves: Opposite, simple and entire, petiole up to 1 cm long, shortly hairy, ovate or elliptical, 1.5–20 cm × 1.5–11 cm.
- Branchlets shortly hairy.
- Flowers: bisexual, regular, fragrant, sepals elliptical to linear, white.
- Fruit composed of 2 long and slender follicles 20–38 cm × 2–9 mm, pale grey to dark brown, many-seeded.
- Seedling with epigeal germination; cotyledons 2–3 mm long.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- Used in treatment of amoebic dysentery.
- The pounded leaves in water are consumed to cure stomach-ache.
- An infusion of the powdered root is taken to treat constipation, asthma, abdominal pains and infertility.
- The root boiled in milk is applied against snakebites and it is also used in the treatment of venereal diseases.
- A decoction of the stem bark is used as a gargle to treat toothache.
- Juice from the fruit is taken to treat cough.
- The bark and leaves are externally applied to cure scabies, boils, ulcers and haemorrhoids.
- A powder prepared from the roots and leaves is given to stop haemorrhages after childbirth and nose bleeding.
- Holarosine and holacurtine, the steroidal part of the molecule is a cardenolide.
- Vitamin: C
- Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Manganese, Potassium, Phosphorus, Sodium, Zinc
- Protein-1.2g/5g
- Carbohydrates-3.4g/5g
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Anti-diabetic
- Anti-diarrhoeal
- Anti-haemorrhoidal
- Antipyretic
- Analgesic
- Antibacterial
- Antifungal
- Anti-amoebic
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antispasmodic
Active Phytochemicals
1. Conarrhimine
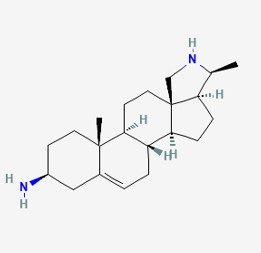
2. Conessine
3. Holantosines a, b, c, d, e and f
.jpg)
4. Holarrhessimine
5. Holarrhidine
6. Holarrhine
7. Holonamine
8. Hydroxyconessine
9. Kurchiline
10. Kurchine
11. Kurchiphylline
12. Norconessine
References
Maroyi, A., 2006. Holarrhena pubescens Wall. ex G. Don. In: Schmelzer, G.H. & Gurib-Fakim, A. (Editors). PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa / Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen, Netherlands. https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Holarrhena_pubescens_(PROTA)
Sinha, Snehadri & Sharma, Aishwarya & Reddy, P. & Rathi, Brijesh & Prasad, N.V.S.R.K. & Vashishtha, Amit (2013). Evaluation of phytochemical and pharmacological aspects of Holarrhena (Wall.): A comprehensive review. Journal of Pharmacy Research. 6. 488–492. 10.1016/j.jopr.2013.04.004.
Zahara, Kulsoom, Sujogya K. Panda, Shasank S. Swain, and Walter Luyten. 2020. "Metabolic Diversity and Therapeutic Potential of Holarrhena pubescens: An Important Ethnomedicinal Plant" Biomolecules 10, no. 9: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091341

