KJC Medicinal Garden
Yashtimadhu
Glycyrrhiza glabra
Order: Fabales
Family: Fabaceae
Genus: Glycyrrhiza
Species: G. glabra
Common Names: Mulaithi, Black sugar
Native to Central and south-western Asia
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
Glycyrrhiza brachycarpa (Boiss)
Glycyrrhiza glandulifera (Waldst & Kit)
Glycyrrhiza hirsute (Pall)
Glycyrrhiza violacea (Boiss)
- Herbaceous plant with stem (0.5-1.5 m tall), erect with a woody base
- Leaves: simple, opposite, green elliptical leaflets (7-15 cm long and 9-17 cm ovate) mildly toothed
- Stem is woody at the base.
- Flowers: Purple or pale whitish blue in colour, open, racemose type of inflorescence
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- Traditionally, licorice has been reported to treat many diseases, such as asthma, tonsillitis, sore throat, hyperdipsia, flatulence, epilepsy, fever, sexual debility, paralysis, heartburn, bleeding etc
- Leaves are used for antibacterial purposes, root extracts show effectiveness against E.coli and E. faecalis and all gram-positive bacteria
- Served as herbal tea, dried powder
- Finds mention in charakasamhita
- Word ‘Mulaithi’ means ‘sweet root’
- Calories: 53 in 13g
- It is fat free
- Licorice provides no significant vitamins or minerals, other than a minimal amount of sodium (7 mg) and potassium
- It’s a protein and fiber free plant.
- Sugars: 9.8 g in 13 g
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Antimicrobial
- Antioxidant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antitussive
- Antidiabetic
- Antiviral
- Anticancer
- Antimutagenic
- Antiulcer
- Hepatoprotective
Active Phytochemicals
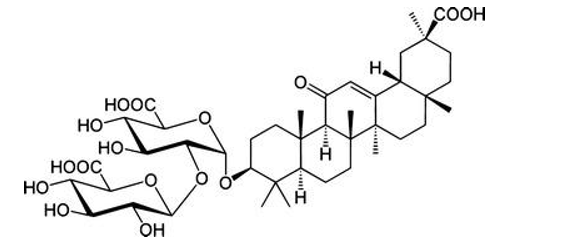
1. Glycyrrhizin
Glycyrrhizin, a triterpenoid compound, accounts for the sweet taste of licorice root. This compound represents a mixture of potassium-calcium-magnesium salts of glycyrrhizic acid that varies within a 2–25 % range. Among the natural saponin, glycyrrhizic acid is a molecule composed of a hydrophilic part, two molecules of glucuronic acid, and a hydrophobic fragment, glycyrrhetic acid. The yellow color of licorice is due to the flavonoid content of the plant, which includes liquiritin, isoliquiritin (a chalcone) and other compounds. The isoflavones, glabridin and hispaglabridins A and B have significant antioxidant activity, and both glabridin and glabrene possess estrogen-like activity
- Glycyrrhetic acid
- Glabridin
- Liquiritin
- Isoliquiritigenin
- Isoflavones
Along with triterpene, saponin, flavonoids, polysaccharides, pectins, simple sugars, amino acids, mineral salts, asparagines, bitters, essential oil, fat, female hormone estrogen, gums, mucilage (rhizome), protein, resins, starches, sterols, volatile oils, tannins, glycosides and various other substances.
References
Hill AF. Economic botany: a textbook of useful plants and plant products. New York: McGarw Hill; Edition 2: 1952
Chopra RN, Nayar SL, Chopra IC. Glossary of Indian medicinal plants. New Delhi: NISCAIR, CSIR; 2002