KJC Medicinal Garden
Hill Mango
Commiphora caudata
Order: Sapindales
Family: Burseraceae
Genus: Commiphora
Species: C.caudata
Common Names: Hill mango, Mavu ,Kiluvai, mamidi
Native to Southern India and srilanka
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
1. C. myrrha
2. C. wightii
3. C. mukul
4. C. africana
5. C.kerstingii
- Flower – axillary panicked cymes.
- Fruit – globose, fleshy drupe, 2-6 valved, seed 1, black with 4 radiating wings.
- Leaf – alternate -spiral, imparipinnate, ovate-oblong.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- This plant is used in curing various ailments like arthritis, hyperlipidemia pain, healing of wounds, coronary artery, gynecological disorders.
- Traditionally the plant parts are used in the treatment of diabetes, ulcer, inflammation, diarrhoea and spasms.
- Leaves of this plant are used to improve digestion and to increase appetite.
- The hill pulayas of Kerala use the leaves of this plant to treat inflammation and pain.
- The endosperm obtained from 4/5 fresh or dried seeds of C. Caudata are taken 2 times a day for 2-3 days to relieve stomach ache.
- The stem and bark are traditionally used in the treatment of rheumatism, ulcers, diarrhoea and spasms.
- The oleo gum resin of the tree is used as incense.
- The gum resin from the bark is used for treating stomach troubles.
- he gum of the stem mixed with water to form mouth washes to cure mouth ulcers.
- Maximum value of organic matter has been found in Commiphora caudata, organic matter also leads to increase in cation exchangeable capacity and quantity of N, K and P.
- P availability is also indicative of the soil PH.
- There are trace elements that are required in micro quantity for optimum growth of plants.
- It requires the amount of micronutrients in the order of Mn>Fe>Cu>Zn.
- Carbohydrates.
- Steroids.
- Protein.
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Anti – arthritic
- Anti- inflammatory
- Anti- bacterial
- Anti-coagulant
- Anti-dicrocoeliasis
- Anti epileptic
- Anti fascioliasis
- Anti fungal
- Anti heterophyidiasis
- Anti hypercholesterolemic
- Anti hyperlipidemic
- Anti obesity
- Anti hypothyroidism
- Anti oxidant
- Anti obesity
- Anti parasitic
- Antiseptic
- Anti ulcer
- Cardio protective
- COX enzyme inhibitory
- Anti carcinogenic /Anti cancer.
Active Phytochemicals
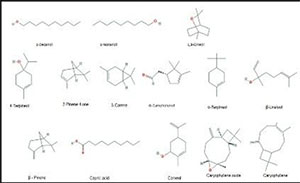
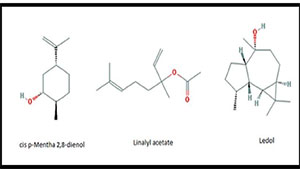
1. In leaf oil : β- pinene (33.7%), cyclofenchene (17.8%), α- terpineol (10.5%), Monoterpene hydrocarbons are major compounds. α-terpineol, verbenol (5.40%), 4-terpineol (3.79%), Myrtenol(3.73%), linalool acetate (2.61%), β-linalool (1.48%) were oxygenated Monoterpene.
2. In fruit: alkaloids, coumarins, flavonoids, terpenoids, phenol, cardiac glycosides, saponins, quinones, steroids, tannins are the major compounds present.
3. In fruit oil: Monoterpene hydrocarbons (32.56) are the major compounds present. Linalool acetate (1.15), thujen-2-one (1.91), myrtenol (0.86), β-linalool (1.23) we’re oxygenated Monoterpene (50.32).
4. In seeds: the C. Caudata plant extract contains 8.21-5.0% (mg/ml) flavonoids, 20.8 + 0.2% (mg/ml) phenol.
5. In root: it was reported that phytochemical screening of roots using various solvents.
Amino Acids, Flavonoids, Glycosides, Protein, tannins, terpenoids, Steroids .
References
McDowell P G, Lwande W S, Deans G, Waterman P G. “Volatile resin exudate from stem bark of Commiphora rostrata, potential role in plant defence.” Phytochemistry vol. 27 (1988): 2519–2521.
Latha S, Selvamani P, Sen D J, Gupta J K, Pal T K, Ghosh L K.” Antibacterial activity of Commiphora caudata and Commiphora berryi leaves.” Indian Drugs vol. 42 (2005): 696–698.

