KJC Medicinal Garden
Turakabevu
Azadirachta indica
Order: Sapindales
Family: Meliaceae
Genus: Azadirachta
Species: A. indica
Common Names: Neem, Nimtree, Margosa tree, Indian lilac
Native to Indo-Burma (South and Southeast Asia)
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
A.excelsa
Melia azaridachta
Melia fraxinifolia
Melia indica
Melia japonica
Melia parviflora
- Fast growing tree (15-20 metres), Erect, Deciduous, Wide spread branches, Roundish dense crown of diameter 20-25m
- Leaves: Opposite, pinnate; reticulate venation, medium to dark green leaflets of about 3-8cm, Terminal leaflet usually absent; Short petioles.
- Fruit is smooth and oval with brown seed coat enclosing 2-3 seeds
- Flowers: White, fragrant, inflorescences bears 250-300 flowers (each 5-6mm long and 8-11mm wide); Protandrous, bisexual.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- The word Azadirachti-Hind in Arabic language means “A freely growing tree of India”
- ‘NEEM’ in Sanskrit means “bestower of Good health”
- Used in 75% of Ayurvedic formulations and Unani.
- The trees bark, flower, fruit, leaves, twigs, seed and seed oil are used to treat stomach ulcers, intestinal worms, leprosy, diabetes, skin diseases, mosquito repellent and astringent.
- Available as capsule, powder, oil, tincture, mouthwash.
- United Nations declares neem as “The tree of the 21st Century”
- Vitamin C & E
- Minerals- Calcium, potassium & phosphorous
- Composition in percentage – Crude protein 13-35; carbohydrates 26-50; fibre 8-26; fat 2-13; ash 5-18
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Anticarcinogenic
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antiulcer
- Antimalarial
- Antioxidant
- Anticancer
- Antidiabetic
- Antifungal
- Wound healing activity
- Radio protective activity
- Immunomodulatory activity
Active Phytochemicals
1. Azadirachtin (dimethyl (1S,4S,5R,6S,7S,8R,11S,12R,14S,15R)-12-acetyloxy-4,7-dihydroxy-6-[(1S,2S,6S,8S,9R,11S)-2-hydroxy-11-methyl-5,7,10-trioxatetracyclo[6.3.1.02,6.09,11]dodec-3-en-9-yl]-6-methyl-14-[(E)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]oxy-3,9-dioxatetracyclo[6.6.1.01,5.011,15]pentadecane-4,11-dicarboxylate)
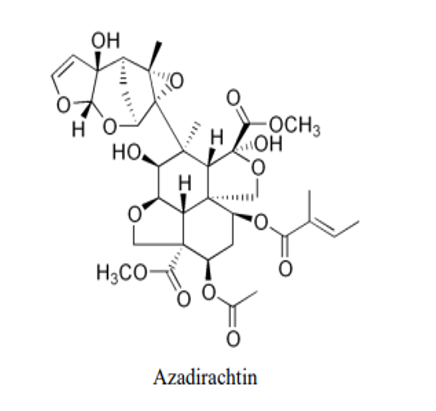
Azadirachtin is a secondary metabolite of neem seeds. It acts as a feeding inhibitor towards many species of insects. It acts as a good antifeedant and is biodegradable. Usually present in the leaves , seeds and bark of neem trees. Azadirachtin is the active ingredient in many pesticides including TreeAzin, AzaMax, BioNEEM, AzaGuard, and Terramera Cirkil. Azadirachtin is synthesised via a biosynthetic pathway using Tirucallol steroid as the precursor.
2. Nimbin ( Methyl (2R,3aR,4aS,5R,5aR,6R,9aR,10S,10aR)-5-(acetyloxy)-2-(furan-3-yl)-10-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1,6,9a,10a-tetramethyl-9-oxo-3,3a,4a,5,5a,6,9,9a,10,10a-decahydro-2H-cyclopenta[b]naphtho[2,3-d]furan-6-carboxylate)
.png)
3. Salannin( [(1R,2S,4R,6R,9R,10R,11R,12S,14R,15R,18R)-14-acetyloxy-6-(furan-3-yl)-10-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)-7,9,11,15-tetramethyl-3,17-dioxapentacyclo[9.6.1.02,9.04,8.015,18]octadec-7-en-12-yl] (E)-2-methylbut-2-enoate)
.png)
4. Sitosterol (17-(5-Ethyl-6-methylheptan-2-yl)-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol )
5. Gedunin (6R,6aS,6bR,7aS,10R,10aS,12bR)-10-(furan-3-yl)-4,4,6a,10a,12b-pentamethyl-3,8-dioxo-3,4,4a,5,6,6a,7a,8,10,10a,11,12,12a,12b-tetradecahydronaphtho[2,1-f]oxireno[d]isochromen-6-yl acetate )
References
Alzohairy MA. Therapeutics Role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and Their Active Constituents in Diseases Prevention and Treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7382506. doi:10.1155/2016/7382506
Srivastava, Santosh & Agrawal, Babita & Kumar, Akhilesh & Pandey, Archana. (2020). Phytochemicals of AzadirachtaIndica Source of Active Medicinal Constituent Used for Cure of Various Diseases: A Review. Journal of scientific research. 64. 285-290. 10.37398/JSR.2020.640153.

