KJC Medicinal Garden
Bilee sooli gida
Aerva lanata
Order: Caryophyllales
Family: Amaranthaceae
Genus: Aerva
Species: Aerva lanata (L.) Juss
Common Names: Mountain knotgrass
Native to Asia, Africa.
Other plants of the same genus with medicinal properties
-
Aerva lanata f. grandifolia Suess.
Aerva lanata f. squarrosa Suess.
Aerva lanata var. citrina Suess.
Aerva lanata var. elegans Suess
- woody root system. The stems are mostly straggling and sprawling and spread widely, sometimes as much as 6 feet (1.8 m) in length.
- Leaves:Stalkless leaves are alternate, oval and 0.5 to 1.5 in (13 to 38 mm) long. They grow from whitish papery stipules with two lobes and red bases
- Stems are hairy
- Flowers: about 0.1 in (2.5 mm) long, pink, green or dull white.
Uses in Tradition systems of medicine
- Aerva lanata is commonly described in Ayurveda as with anti-inflammatory.
- Antihelmintic, anti-bacterial and mild analgesic effects.
- It is used in the treatment of lithiasis, cough, asthma, and headache and as an antidote for rat poisoning.
- Alpha Amyrin.
- Beta Sitoterol
- Comsterol
Suggested Medicinal Properties
- Antioxidant Properties
- Lowers Blood Sugar Levels
- Treats Asthma
- Treats Diarrhea
- Anti Urolithiatic Activite
- For Getting Rid Of Intestinal Worms
- Anti Cancer Properties
- Protects The Kidneys
Active Phytochemicals
The whole plant of A.lanata showed the presence of the following phytochemical
1. Flavonoids
Flavonoids, a group of natural substances with variable phenolic structures, are found in fruits, vegetables, grains, bark, roots, stems, flowers, tea and wine. These natural products are well known for their beneficial effects on health and efforts are being made to isolate the ingredients so called flavonoids.
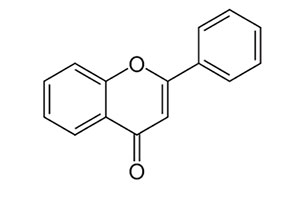
2. Terpenoids :
Terpenoids are volatile substances which give plants and flowers their fragrance. They occur widely in the leaves and fruits of higher plants, conifers, citrus and eucalyptus. The term terpene' was given to the compounds isolated from terpentine, a volatile liquid isolated from pine trees.
3. Glycosides :
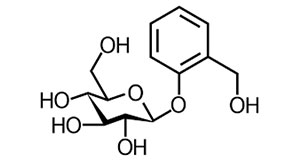
4. Saponins
5. Resins
6. Carbohydrates
7. Proteins
References
1.1.Gullo VP, Hughes DE. Exploiting new approaches for natural product
drug discovery in the biotechnology industry. Drug Discov Today
Technol 2005;2(3):281-6.
2. Vital PG, Rivera WL. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of
Chromolaena odorata (L. F) King and Robinson and Uncaria perrottetii
(A. Rich) Merr extracts. J Med Plants Res 2009;3(7):511-8.
3. Harmmer MM, Benice B, David L. Herbal alternative medicine use in
an urban dental hygiene clinic. J Dent Hyg 2006;1:19.

